THE BENEFICIAL EFFECT OF MRET SHIELD ON BLOOD MORPHOLOGY IN VITRO FOLLOWING THE EXPOSURE TO ELECTROMAGNETIC RADIATION
The beneficial effect of EMR shielding material (MRET-Shield) on human blood in vitro was observed at the laboratory of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, USA. The effect of the computer monitor radiation on human blood samples (22 samples in each group) was studied with and without installation of MRET-Shield and compared to the control group not exposed to EMR. The blood samples were exposed to the computer monitor radiation at the distance of 15” (0.38 meter) for one hour. Test results are statistically valid with p<0.01.
The White Blood Cells (WBC) consist of Granulocytes (GRAN), Lymphocytes (LYM), and “Minimum Inhibitory Dilution,” a measure of rare cells and a number of precursor white cells (MID). The exposure of the blood samples to external EMR of the computer monitor led to the changes in the ratio of WBC components, particularly to the changes in Granulocytes, Lymphocytes and MID counts (measured in %). The installation of MRET-Shield EMR shielding device) on the computer monitor significantly reduced the level of changes of Granulocytes and Lymphocytes counts and almost did not affect the level of changes in the MID count. These results confirm the reduction of stress following the exposure of blood samples to EMR in case of the installation of MRET-Shield on the computer monitor.
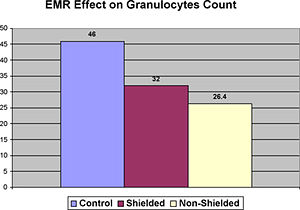
Granulocytes are a critical component of WBC and play an important role in the immune system reactions. Their decrease is not beneficial for body homeostasis. The experiment revealed a decrease of Granulocytes in blood samples exposed to electromagnetic radiation. It also showed that the installation of MRET-Shield on the computer monitor reduced the level of changes in Granulocytes count by 29%.
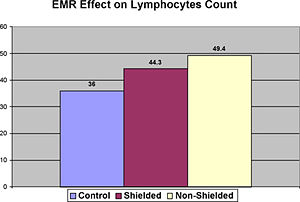
An increase in the Lymphocytes count is associated with a physiological response to an antigenic or inflammatory stimulus and infection or other kind of external stress. The general consensus is that the increase of Lymphocytes above normal level in case of the absence of any infections increases the risk of leukemia, lymphomas, and other disorders. The experiment revealed the increase of Lymphocytes in blood samples exposed to the computer monitor radiation. It also showed that the installation of MRET-Shield on the computer monitor reduced the level of changes in Lymphocytes count by 38%.
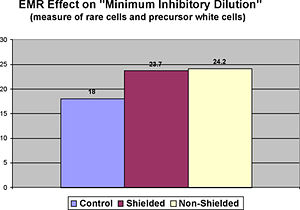
The experiment revealed the increase of MID count for blood samples exposed to the computer monitor radiation. The reduction of the level of changes in the MID count after the installation of MRET-Shield was insignificant.
CONCLUSION
The experiment revealed the decrease of Granulocytes count and the increase of Lymphocytes and MID (precursor white cells) counts in both cases. There were no significant changes in the total quantity of WBC. It also showed that the installation of MRET-Shield on the computer monitor significantly reduced the level of changes in the ratios of Granulocytes and Lymphocytes counts.
The changes in the ratio of GRAN were reduced by
(32 – 26.4)/(46 – 26.4) = 5.6/19.6 = 29%
The changes in the ratio of LYM were reduced by
(49.4 – 44.3)/(49.4 – 36) = 5.1/13.4 = 38%
The changes in the ratio of MID were insignificantly reduced by
(24.2 – 23.7)/(24.2 – 18) = 0.5/6.2 = 8%
Thus, the combined changes in the ratios of GRAN, LYM, and MID following the exposure to EMR of the computer monitor were:
without MRET-Shield 19.6 (GRAN) + 13.4 (LYM)+ 6.2 (MID) = 39.2%
with MRET-Shield 14 (GRAN) + 8.3 (LYM) + 5.7 (MID) = 28%
This calculation shows that the installation of MRET-Shield on computer monitor reduced the level of combined changes in the content of White Blood Cells count (GRAN, LYM and MID) by (39.2 – 28)/39.2 = 29% in this experiment.
This experiment provides evidence that the exposure of human blood samples in vitro to EMR of the computer monitor affects the ratio of Granulocytes and Lymphocytes in WBC. This effect is related to the stress response and can affect cellular process related to the blood morphology such as growth, division, and death of cells in all types of WBC. The installation of MRET-Shield on the computer monitor significantly reduced the effect of EMR on the ratio of WBC components (by 29%) and the blood morphology. The results are statistically valid with p<0.01.
